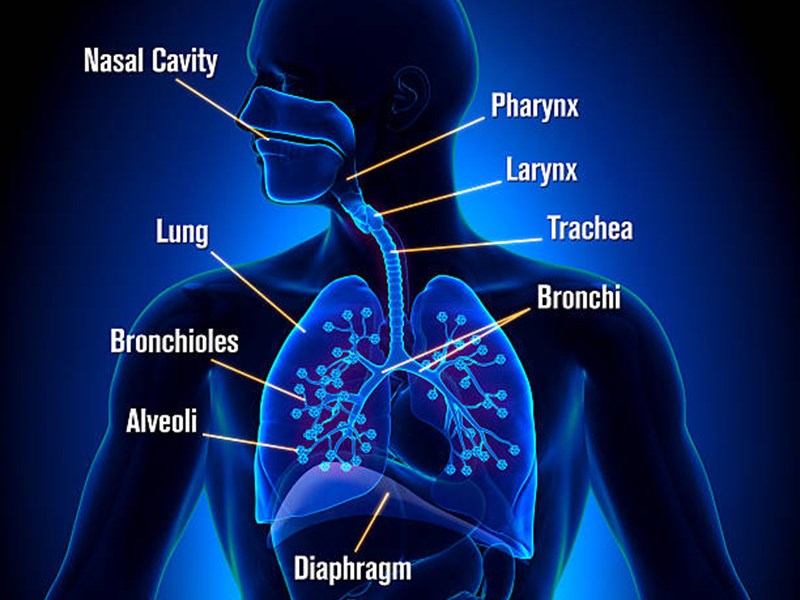
Respiratory System
Respiratory system: It is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles
Anatomy
The body needs energy for survival. Most of this energy can only be produced in the presence of oxygen. The waste product of this energy production is carbon dioxide. The respiratory system is responsible for supplying oxygen and the excretion of carbon dioxide.
The respiratory system consists of the following organs:
· Nose
· Pharynx
· Larynx
· Trachea
· Bronchi
· Bronchioles
· Lungs
· Muscles – intercostal muscles and diaphragm
The Nose
The function of the nose is to warm, moisten and filter inhaled air.
The air is warmed by the blood vessels lining the nasal cavity.
The air is moistened by the mucosa covering the nasal cavity.
Hairs in the front of the nasal cavity trap larger particles and the smaller particles are filtered by the mucosa.
Nerve endings in the nose are stimulated by chemical substances given off by odorous materials. These impulses are conveyed by the olfactory nerves to the brain where the sensation of smell is perceived.
The nasal cavity opens into the paranasal sinuses:
· Maxillary sinuses
· Frontal and sphenoid sinuses
· Ethmoid sinuses.
The sinuses function in speech and also lighten the skull.
The Pharynx
The pharynx is a passageway for both air and food.
Air is warmed and moistened by the pharynx.
Olfactory nerve endings in the pharynx play a role in taste.
The tonsils are situated in the pharynx and produce antibodies in response to infections.
The pharynx gives the voice its’ individual characteristics.
The auditory tube extends from the pharynx to the middle ear, and assists with hearing.
The Larynx
The larynx (or voice box), extends from the root of the tongue to the trachea. It is composed of several irregularly shaped cartilages.
The larynx controls the pitch, volume, and resonance of the voice.
The vocal cords produce sound.
The epiglottis closes during swallowing to ensure that food does not enter the lungs.
The Trachea
The trachea is composed of 16 to 20 C-Shaped rings of hyaline cartilage.
The trachea supports the movement of air into and from the lungs.
Cilia lining the trachea move mucous up towards the larynx to be expelled.
Nerve endings in the trachea are sensitive to the presence of particles and this stimulates the cough reflex.
The Bronchi
The brochi are lined with columnar epithelium. This ensures the removal of particles from the air.
The bronchi warm and moisten the air.
Nerve endings also stimulate the cough reflex.
The bronchioles and alveoli
The alveoli are tiny sacs at the end of the bronchioles. This is where gas exchange occurs. The walls become gradually thinner and are lined with squamous epithelium. The alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries. Gases move from a higher concentration to a lower concentration by means of diffusion. Therefore oxygen moves from the alveoli into the capillaries and carbon dioxide moves from the capillaries into the alveoli.
Lymphocytes and plasma cells produce antibodies to protect against pathogens.
The Lungs
The lungs are surrounded by the pleura. One layer is attached to the wall of the thoracic cavity and the other layer is attached to the lung. Between these 2 layers is a serous fluid, allowing the 2 layers to glide over one another.
The pulmonary artery supplies deoxygenated blood to the lungs, and the pulmonary veins leave the lungs with oxygenated blood.
The muscles of respiration
Intercostal muscles are arranged in 2 layers between the ribs, external and internal intercostals muscles. When they contract they pull the ribs outwards and upwards therefore enlarging the thoracic cavity.
The diaphragm forms the floor of the thoracic cavity. When it contracts it moves downwards and enlarges the thoracic cavity.
The diaphragm and intercostals muscles contract at the same time to enlarge the thoracic cavity.
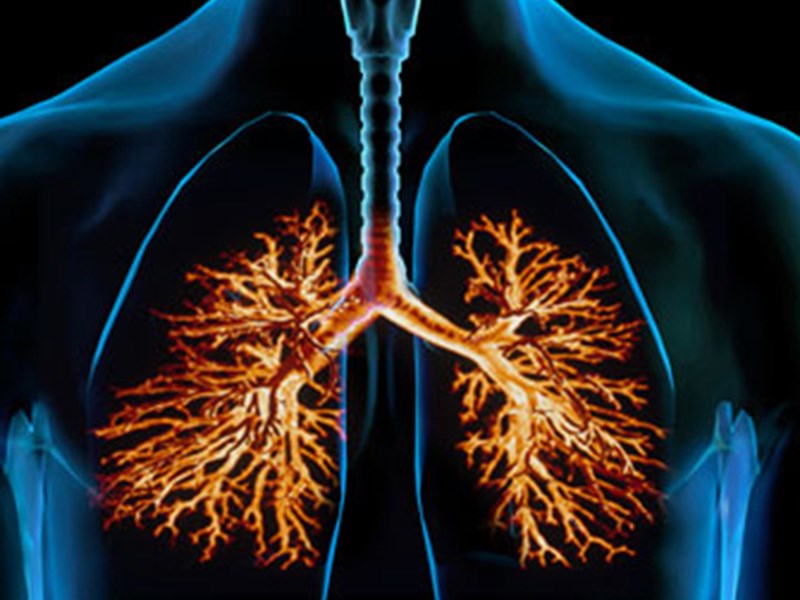
Bronchitis
What is acute bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is an infection of the bronchial tree. The bronchial tree is made up of the tubes that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes get infected, they swell and mucus forms inside them. This makes it hard for you to breathe.
What are the symptoms of acute bronchitis?
The symptoms of acute bronchitis can include:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- A cough that may bring up yellow or green mucus
- Chest congestion
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chills
- Body aches
What causes acute bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is almost always caused by viruses that attack the lining of the bronchial tree and cause infection. As your body fights back against these viruses, more swelling occurs and more mucus is produced. It takes time for your body to kill the viruses and heal the damage to your bronchial tubes.
In most cases, the same viruses that cause colds cause acute bronchitis. Research has shown that bacterial infection is a much less common cause of bronchitis than we used to think. Very rarely, an infection caused by a fungus can cause acute bronchitis.
How do people get acute bronchitis?
The viruses that cause acute bronchitis are sprayed into the air or onto people’s hands when they cough. You can get acute bronchitis if you breathe in these viruses. You can also get it if you touch a hand that is coated with the viruses.
If you smoke or are around damaging fumes (such as those in certain kinds of factories), you are more likely to get acute bronchitis and to have it longer. This is because your bronchial tree is already damaged.
You should call your doctor if:
- You continue to wheeze and cough for more than 2 weeks, especially at night when you lie down or when you are active.
- You continue to cough for more than 2 weeks and sometimes have a bad-tasting fluid come up into your mouth. This may mean you have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is a condition in which stomach acid gets into your esophagus (windpipe).
- You have a cough that produces blood, you feel very sick and weak, you have a high fever that doesn’t go down and you are short of breath. You may have pneumonia.
How is acute bronchitis treated?
Most cases of acute bronchitis will go away on their own after a few days or a week. It's a good idea to get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids (for example, water and fruit juices) and increase the humidity in your environment. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever (such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen) to ease pain and lower fever. It is okay to take an over-the-counter cough suppressant if your cough is dry (not producing any mucus). It's best not to suppress a cough that brings up mucus because this type of cough helps clear the mucus from your bronchial tree faster.
If you smoke, you should quit. This will help your bronchial tree heal faster.
Some people who have acute bronchitis need medicines that are usually used to treat asthma. If you hear yourself wheezing, this indicates you may need asthma medicines. These medicines can help open the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus. They are usually given with an inhaler. An inhaler sprays the medicine right into the bronchial tree. Your doctor will decide if this treatment is right for you.
How long will the cough from acute bronchitis last?
Sometimes the cough from acute bronchitis lasts for several weeks or months. Usually this happens because the bronchial tree is taking a long time to heal. However, a cough that doesn’t go away may be a sign of another problem, such as asthma or pneumonia.
How can I keep from getting acute bronchitis again?
One of the best ways to keep from getting acute bronchitis is to wash your hands often to get rid of any viruses.
If you smoke, the best defense against acute bronchitis is to quit. Smoking damages your bronchial tree and makes it easier for viruses to cause infection. Smoking also slows down the healing process, so it takes longer for you to get well.
Boost your immune system.
Chronic Bronchitis
What is chronic bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation (or irritation) of the airways in the lungs. Airways are the tubes in your lungs that air passes through. They are also called bronchial tubes. When the airways are irritated, thick mucus forms in them. The mucus plugs up the airways and makes it hard for air to get into your lungs. Symptoms of bronchitis include a cough that produces mucus (sometimes called sputum), trouble breathing and a feeling of tightness in your chest.
"Chronic" means that the condition last a long time. Chronic bronchitis is bronchitis that lasts longer than 3 months. Chronic bronchitis often occurs with emphysema, and together these diseases are called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What causes chronic bronchitis?
Cigarette smoking is the main cause of chronic bronchitis. When tobacco smoke is inhaled into the lungs, it irritates the airways and they produce mucus. People who have been exposed for a long time to other things that irritate their lungs, such as chemical fumes, dust and other substances, can also develop chronic bronchitis.
How does my doctor know if I have chronic bronchitis?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms: Are you coughing up mucus? Are you having trouble breathing? Does your chest feel tight? How long have you had these symptoms? Do you smoke cigarettes? How many cigarettes do you smoke each day? How many years have you been smoking? Have you been breathing in other things that can irritate your lungs?
If your doctor thinks you have chronic bronchitis, you may be tested to find out if your lungs are damaged. You might have a pulmonary function test to see how well your lungs are working. During this test, you breathe into a machine that measures the amount of air in your lungs. Your doctor may also order blood tests and a chest X-ray.
What can I do to help my breathing and reduce my coughing?
If you smoke, the most important thing you can do is to stop. The more smoke you breathe in, the more it damages your lungs. If you stop smoking, you'll breathe

Colds And Flu
Although the common cold and the flu share many similar symptoms, they are two different conditions.
The symptoms of a cold develop slowly and can include:
- Fever up to 39 degrees Celsius
- Runny or stuffy nose (often with green- or yellow-colored discharge)
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Sneezing
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Watery eyes
What is H1N1 flu?
The H1N1 influenza (also called swine influenza or swine flu) is a respiratory infection caused by a virus found in pigs. H1N1 flu can infect humans.
Cold symptoms are generally more mild than flu symptoms.
Flu symptoms usually appear suddenly and can include:
- Fever over 39 degrees Celsius
- Stuffy nose
- Nausea
- Chills and sweats
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches, especially in your back, arms and legs
- Cough
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
What causes colds and the flu?
Viruses cause the common cold and the flu. Over 200 different viruses can cause colds. There are not as many viruses that cause the flu.
What can I do to feel better?
There's no cure for the common cold. All you can do to feel better is treat your symptoms while your body fights off the virus.
Ways to treat your cold and flu symptoms
- Get plenty of rest, especially while you have a fever. Rest helps your body fight infection.
- Stop smoking and avoid secondhand smoke, which can make cold symptoms worse.
- Drink lots of fluids such as water and clear soups. Fluids help loosen mucus. Fluids are also important because they help prevent dehydration.
- Gargle with warm salt water a few times a day to relieve a sore throat. Throat sprays or lozenges may also help relieve the pain.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Use saline (salt water) nose drops to help loosen mucus and moisten the tender skin in your nose.
What's in over-the-counter cold and flu medicines?
The ingredients listed below are found in many cold and flu medicines. Read labels carefully. If you have questions, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
- Analgesics relieve aches and pains and reduce fever. Warning: Children and teenagers shouldn't be given aspirin because it can cause Reye's Syndrome.
- Antitussives (also called cough suppressants) tells your brain to stop coughing. Don't take an antitussive if you're coughing up mucus. Warning: Children under 4 years of age shouldn't be given cough medicines.
- Expectorants help thin mucus so it can be coughed up more easily.
- Decongestant nasal sprays shrink the nasal passages and reduce congestion. Adults should only use these medicines for a few days. Overuse can cause symptoms to get worse when you stop using the nasal spray. Warning: Children shouldn't use these medicines at all.
Call your doctor if you have these cold and flu symptoms:
In children:
- High fever(above 39 degrees celcius), or a fever that lasts for more than 3 days
- Symptoms that last for more than 10 days
- Trouble breathing, fast breathing or wheezing
- Bluish skin color
- Earache or drainage from the ear
- Changes in mental state (such as not waking up, irritability or seizures)
- Flu-like symptoms that improve, but return with a fever and a worse cough
- Worsening of a chronic medical condition (such as diabetes or heart disease)
- Vomiting or abdominal pain
In adults:
- A high, prolonged fever (above 39 degrees celcius) with fatigue and achiness
- Symptoms that last for more than 10 days or get worse instead of better
- Trouble breathing or shortness of breath
- Pain or pressure in the chest
- Fainting or feeling like you are about to faint
- Confusion or disorientation
- Severe or persistent vomiting
- Severe sinus pain in your face or forehead
- Very swollen glands in the neck or jaw
Can I prevent catching a cold or the flu?
You can reduce your risk of catching a cold or the flu by washing your hands frequently, which stops the spread of germs. Eating healthy, exercising and getting enough sleep also play a part in preventing colds and the flu because they help boost your immune system.
If you are sick, make sure that you cover your mouth when you cough and wash your hands often to prevent giving your cold or flu to others.
Respiratory Treatment Table
Echinacea
Herbal
Echinacea is mostly used as an immune modulator to aide the body in fighting or preventing infections, such as the common cold, flu, and chronic infections such as respiratory and lower urinary tract infections. In addition, there have been a few studies that support its use for chronic candidiasis. Echinacea acts as a stimulant to the immune system by several methods. It may increase the production of specific types of white blood cells. The active components of Echinacea are phenolic compounds, terpenoid compounds, nitrogenous compounds, such as alkylamides and alkaloids, and carbohydrates, such as polysaccharides. Polysaccharide components have been proven to activate macrophages (stimulation of phagocytosis), increase leukocyte mobility, and increase cellular respiration that may lead to the attack of tumor cells (increased tumor necrosis factor) and microorganisms. Echinacea also strengthens human cell walls so bacteria and viruses have a harder time getting into cells. It is probably best known as a preventative and treatment for viral upper respiratory infections, such as colds and the flu.
For general immunesupport, take 250mg to 500mg every day during the winter months. During and acute attack of cold and flu, take 250mg to 500mg 3 times a day at the onset of the symptoms for 5 days and thereafter take 500mg daily. If you suffer from an auto-immune disorder, avoid using Echinacea. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using this product.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Olive Leaf
Herbal
Olive leaf extract is very beneficial for treating conditions caused by viruses, retrovirus, bacteria, as well as protozoa. It interferes with the critical amino acid production of viruses and may inactivate the virus by virus budding or assembly. It can also penetrate the cells and stop viral replication. It furthermore is effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, fungi and yeast strains and stops the production of micro-toxins, which contribute to chronic fatigue. People with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome have reported a radical improvement when taking olive leaf extract internally and report more energy and a better sense of wellbeing. Olive leaf extract further improves candida infections and the resultant vaginal discharge, psoriasis, PMS, weight problems, headaches and all other symptoms that coincide with yeast infections. People struggling with the Epstein Barr virus have also reported dramatic improvement.
For general use take 400mg per day. If you suffer from low blood pressure, use Olive leaf with caution. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should avoid using the product.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Vitamin C
Nutritional
Vitamin C is probably best known for its effects as an antioxidant and its role in maintaining proper immune function. Because of vitamin C's role in maintaining normal immune function, a lot of people use it for treating and preventing infectious conditions such as the common cold. T-lymphocyte activity, phagocyte function, leukocyte mobility, and possibly antibody and interferon production seem to be increased by vitamin C. Vitamin C levels in phagocytes and lymphocytes are up to 100 times greater than in plasma. Some researchers think that vitamin C levels in white blood cells decrease at the onset of a cold and that boosting vitamin C intake might be beneficial. There is some evidence vitamin C might have other effects in patients with the common cold. Vitamin C might protect normal tissues against reactive oxygen species that are produced by phagocytes during a viral infection. It might also enhance the proliferative responses of T-lymphocytes. There is preliminary evidence vitamin C excretion might actually decrease during a cold, indicating that patients may retain vitamin C. However, absorption of vitamin C is unchanged during a cold. The RDA for vitamin C is 60mg - this prevents deficiency symptoms.
During the winter months take 500mg per day to boost immune function. During an attack of cold and flu, take 2000mg per day for 3 days. Pregnant women should not take more than 1000mg of Vitamin C per day.
L-Lysine
Amino Acid
Taking lysine orally reduces recurrences of herpes simplex labialis infections (cold sores), and reduces the severity and healing time of herpes simplex labialis infections.
Take 1000mg 3 times a day for the first 2 weeks. Thereafter maintain with 500mg every second day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using this product.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
N-acetyl cysteine
Amino Acid
N-acetyl cysteine is the N-acetyl derivative of the amino acid L-cysteine. N-acetyl cysteine is a precursor of glutathione, which is a potent antioxidant. Glutathione can not cross the cell membrane, but N-acetyl cysteine easily crosses the cell membrane where it is converted to cysteine and, subsequently, glutathione. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl-free radicals reduce intracellular and extracellular concentrations of glutathione. N-acetyl cysteine is a very efficient way to replenish glutathione and reduce damage caused by ROS. N-acetyl cysteine is able to break down mucous in the respiratory tract and therefore aids in the treatment of respiratory infections.
For general use, take 250mg to 500mg daily. During a respiratory tract infection, take 1000mg daily for 5 days. If you suffer from asthma, consult your healthcare practitioner before using this product.. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using this product.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
L-Glutathione
Amino Acid
Glutathione may inhibit the activity of enzymes that help the flu virus colonize cells lining the mouth and throat. Flu-infected mice fed glutathione-enriched drinking water have lower tissue virus levels than untreated mice. Human studies are needed to determine the effects of glutathione on flu infection.
For general use, take 50mg daily. During a respiratory tract infection, take up to 250mg daily for 5 days. If you suffer from asthma, consult your healthcare practitioner before using this product.. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid using this product.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Selenium
Nutritional
Selenium has antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are believed to protect body cells from damage caused by oxidation, the chemical breakdown of foods into components the body can use. Oxidation also produces by-products known as oxygen free radicals, which may suppress immune function.
Take 50mcg to 200mcg per day. Never take more than 200mcg of Selenium per day. Pregnant women should not take more than 60mcg per day.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Zinc
Nutritional
Zinc has an effect against viruses. There's some evidence that zinc also has antiviral activity against the herpes virus. Plasma zinc levels are low in people with HIV infection, but this appears to be a marker of disease progression rather than an indication of zinc deficiency. Other evidence suggests that avoiding zinc deficiency might allow normal or improved immune function, particularly T-lymphocyte mediated cellular immunity. It also might inhibit susceptibility of T-lymphocytes to apoptosis.
For general use take 15mg to 30mg per day. Never take more than 80mg of zinc per day.









Sinus
What are sinuses?
Sinuses are the air chambers in the bone behind your cheeks, eyebrows and jaw. They make mucus, a fluid that cleans bacteria and other particles out of the air you breathe. Tiny hairs called cilia sweep mucus out of your sinuses so it can drain out through your nose.
What is sinusitis?
Sinusitis is the name for a condition in which the lining of your sinuses becomes inflamed.
What causes sinusitis?
Anything that causes swelling in your sinuses or keeps the cilia from moving mucus can cause sinusitis. This can occur because of changes in temperature or air pressure. Allergies can cause sinusitis. Using decongestant nasal sprays too much, smoking, swimming or diving can also increase your risk of getting sinusitis. Some people have growths called polyps that block their sinus passages and cause sinusitis.
When sinusitis is caused by a bacterial or viral infection, you get a sinus infection. Sinus infections sometimes occur after you’ve had a cold. The cold virus attacks the lining of your sinuses, causing them to swell and become narrow. Your body responds to the virus by producing more mucus, but it gets blocked in your swollen sinuses. This built-up mucus is a good place for bacteria to grow. The bacteria can cause a sinus infection.
What are the symptoms of sinusitis?
The symptoms of sinusitis include:
- Pain or pressure in the forehead, cheeks, nose and between the eyes
- Headache
- Fever
- Nasal congestion
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Cough, which may be worse at night
- Bad breath (called halitosis)
- An ache in the teeth
How is acute sinusitis treated?
Treatment for sinusitis depends on the cause.
You can use a saline nasal spray, which will clean our your nasal passages and help clear congestion. Your doctor may recommend a prescription nasal spray that helps treat inflammation.
If you have sinus pain or pressure, your doctor may prescribe or recommend a decongestant to help your sinuses drain. Decongestants are generally only recommended for short-term use.
If your case of sinusitis is very severe and your doctor thinks the cause is bacterial, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic. You may take an antibiotic for 10 to 14 days, but you will usually start feeling better a couple of days after you start taking it. It is important to take antibiotics exactly as your doctor tells you and to continue taking it until it is completely gone, even after you’re feeling better.
If allergies are causing your sinusitis, your doctor may treat the allergy. Then the sinusitis will usually clear up on its own.
Tips on taking care of sinusitis
- Get plenty of rest. Lying down can make your sinuses feel more stopped-up, so try lying on the side that lets you breathe the best. You can prop yourself up with a pillow.
- Sip hot liquids and drink plenty of fluids.
- Apply moist heat by holding a warm, wet towel against your face or breathing in steam through a cloth or towel. This will relieve sinus pressure and help open your sinus passages.
- Talk with your doctor before using an over-the-counter cold medicine. Some cold medicines can make your symptoms worse or cause other problems.
- Don’t use a nasal spray with a decongestant in it for more than 3 days. If you use it for more than 3 days, the swelling in your sinuses may get worse when you stop using the medicine.
Avoid alcohol, which can worsen swelling in the sinuses.